
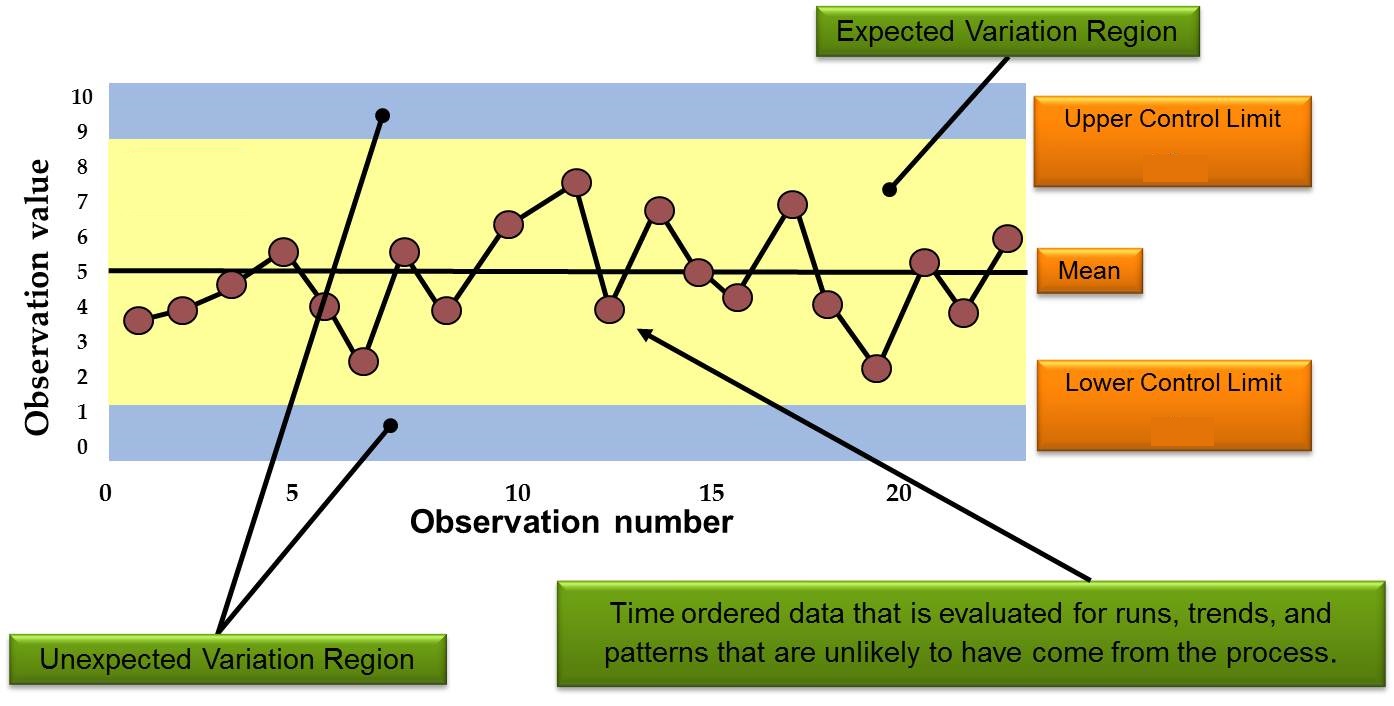
Measurements: Time to reach office – the time taken on daily basis to reach office from home is measured to monitor the system/process. Now, relating our example with the definition above: However, on one fine day you leave from your home and you reach office in 60 minutes because there was an accident on the way and the entire traffic was diverted which caused additional delay of around 20 minutes. There is a variation of 5 minutes less or more because of slight traffic or you get all the traffic signals red on your way. The average time it takes you to reach office is 35 minutes while in most of the cases it takes 30 to 40 minutes for you to reach office. You leave for office from your home every day at 9:00 AM. Let’s take an example and understand it step by step using above definition. Using control charts is a continuous activity, ongoing over time.” “Common” sources, because they are an expected part of the process, are of much less concern to the manufacturer than “assignable” sources. Control charts attempt to differentiate “assignable” (“special”) sources of variation from “common” sources. Let’s understand what are control charts and how are they used in process improvement.Īccording to Wikipedia, “The data from measurements of variations at points on the process map is monitored using control charts. Statistical process control can be used to monitor the processes and ensure that the desired quality level is maintained.Ĭontrol chart is the primary statistical process control tool used to monitor the performance of processes and ensure that they are operating within the permissible limits. One of the techniques that can be used in control phase is statistical process control. You have implemented new processes and now, you have to ensure that any deviations in the optimized processes are corrected before they result in any defects. You have to think of new ways using techniques such as design of experiments and set up pilot projects to test the idea. In this phase, you need to find out ways or methodologies to work on the problem and improve the current processes. Now, you are aware about the entire process and cause behind the problems. Instead, it should be a complete fact-based and data-driven exercise to identify the root cause. In this phase, make sure that your biases don’t lead you to results. Based on the goal defined in the ‘Define’ phase, you understand the process in detail and collect relevant data which is to be used in subsequent phases.īy this phase, you know the goal that are you trying to achieve and also, you understand the entire process and have the relevant data to diagnose and analyze the problem. Understanding the ‘As-Is’ state of the process. There should be clarity on ‘Why is the project being undertaken?’ In this stage, everyone involved in the project understands his/her role and responsibilities. DMAIC methodology has five phases:ĭefining the goals that you wish to achieve – basically, identifying the problem statement you are trying to solve. Since this article talks about control charts, we will focus on DMAIC project methodology of which control charts is a part of. DMAIC methodology is used for projects aimed at improving existing business processes while, DMADV is used for projects which aims at creating new processes. Six Sigma projects follow methodologies which are called as DMAIC and DMADV. Six Sigma uses empirical and statistical quality management methods to carry out operational improvement and excellence projects in organizations. At the heart of Six Sigma lies the core strategies to improve the quality of processes by identifying and removing the causes leading to defects and variability in product quality and business processes. Six Sigma was popularized by manufacturing organizations and Jack Welch, former CEO of GE, was one of advocators of Six Sigma. Six Sigma is a set of techniques used by organizations to improve their processes and optimize operations. I am sure you must have heard of Six Sigma quality standard or Six Sigma experts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
